An income statement is a financial statement that reports the revenues and expenses of a company over a specific accounting period. It shows whether a company has made a profit or loss during that period. It is also known as the , where profit or loss is determined by subtracting all expenses from the revenues of a company. An income statement shows how effective the strategies set by the management at the beginning of an accounting period are. It also helps business owners determine whether they can generate high profit by increasing prices, decreasing costs, or both. Businesses have two reporting options when preparing an income statement. They can create a multi-step income statement or a single-step income statement. A multi-step income statement includes the same general information found in a single-step income statement. However, it uses multiple equations to determine the net profit of the company. It segregates total revenue and expenses into operating and non-operating heads. This means that revenues and expenses are classified whether they are part of the primary operations of the business or not. The multi-step income statement reflects comprehensively the three levels of profitability - gross profit, operating profit, and net profit. The multi-step income statement provides an in-depth analysis of the financial performance of a business in a specific reporting period by using these profitability metrics. This makes it easier for users of the income statement to better comprehend the operations of the business. Revenue is the income generated from normal business operations. It is displayed at the top line of an income statement. Depending on the company, revenue can also be called “sales revenue” or “sales.” COGS is a line item that compiles the direct costs associated with creating the products to generate revenue. It is also referred to as the cost of sales if the company is offering services. Direct costs can include parts, labor, materials, and other expenses directly related to production. Gross profit is calculated by subtracting COGS from revenue. This metric evaluates the efficiency of a company at utilizing its labor and supplies in producing its goods or services. Operating expenses are the expenses the company incurs through its normal day-to-day operations. It includes marketing costs, rent, inventory costs, equipment, payroll, step costs, insurance, and funds intended for research and development. Operating expenses are basically the selling, general, and administrative costs, depreciation, and amortization of assets. What Is an Income Statement?
Multi-Step Income Statement

Components of a Multi-Step Income Statement
Revenue
Cost of Goods Sold
Gross Profit
Operating Expenses
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) permits businesses to deduct operating expenses if the business operates to gain profits.
Operating Profit
Operating profit shows what is earned from regular business operations.
This is the profit before any non-operating income and non-operating expenses are taken into account.
Operating profit is gross profit minus operating expenses.
Non-Operating Items
Non-operating items are further classified into non-operating revenue and non-operating expenses.
Non-operating revenues are revenues that a company earns from activities that are not related to its primary business operations.
These include dividend income, and proceeds from sale of extraordinary items.
Non-operating expenses are the costs from activities not related to a company’s core business operations.
These include payments to settle lawsuits.
Earnings Before Interest and Taxes (EBIT)
EBIT is the resulting figure after all non-operating items, excluding interest and taxes, are factored into operating profit.
EBIT is helpful when analyzing the performance of the operations of a company without the costs of the tax expenses and capital structure impacting profit.
Interest Expense
Interest expenses are expenses incurred by a business for borrowed funds. This item is deducted from EBIT to come up with earnings before tax.
Earnings Before Taxes (EBT)
EBT, also referred to as pre-tax income, measures a company’s profitability before income taxes are accounted for.
This is the last subtotal before arriving at net profit.
Taxes
Income taxes are taxes imposed by governments on income generated by individuals and businesses within their jurisdiction.
This is used to fund public services, provide goods for citizens, and pay government obligations.
Net Profit
Net profit, also known as net income, is the amount left after deducting income taxes from EBT.
This represents the profit that a company has earned for the period, after taking into account all expenses.
Example of a Multi-Step Income Statement

The illustration above comprehensively shows the different levels of profitability of XYZ Corporation.
It starts with the top-line item which is the sales revenue amounting to $90,000.
From this amount, the cost of goods sold amounting to $47,000 is deducted in order to arrive at the first level of profitability which is the gross profit.
Operating expenses totaling $37,000 were then deducted from the gross profit to arrive at the second level of profitability - operating profit which amounted to $6,000.
After taking into account all non-operating items, the bottom line of the company showed $7,000 as net profit.
Single-Step Income Statement
A single-step income statement displays the revenue, expenses, and gains or losses generated by a company.
It reports these figures by using just one equation to calculate profits.
The equation used in a single-step income statement is:

A single-step income statement is useful when your business does not have complex operations or only needs a simple statement that could report the net income of a business.
It is also practical to use this format when you do not need to separate operating expenses from the cost of sales.
Components of a Single-Step Income Statement
Revenues & Gains
Revenues are the result of the company’s primary business activities.
Gains represent all other sources of income apart from the company’s main business activities.
Examples of gains are proceeds from the disposal of assets, and interest income.
Expenses & Losses
Expenses are how much it costs for a business to keep running and make money.
Losses can be the result of one-time or any other extraordinary expenses, or lawsuit expenses.
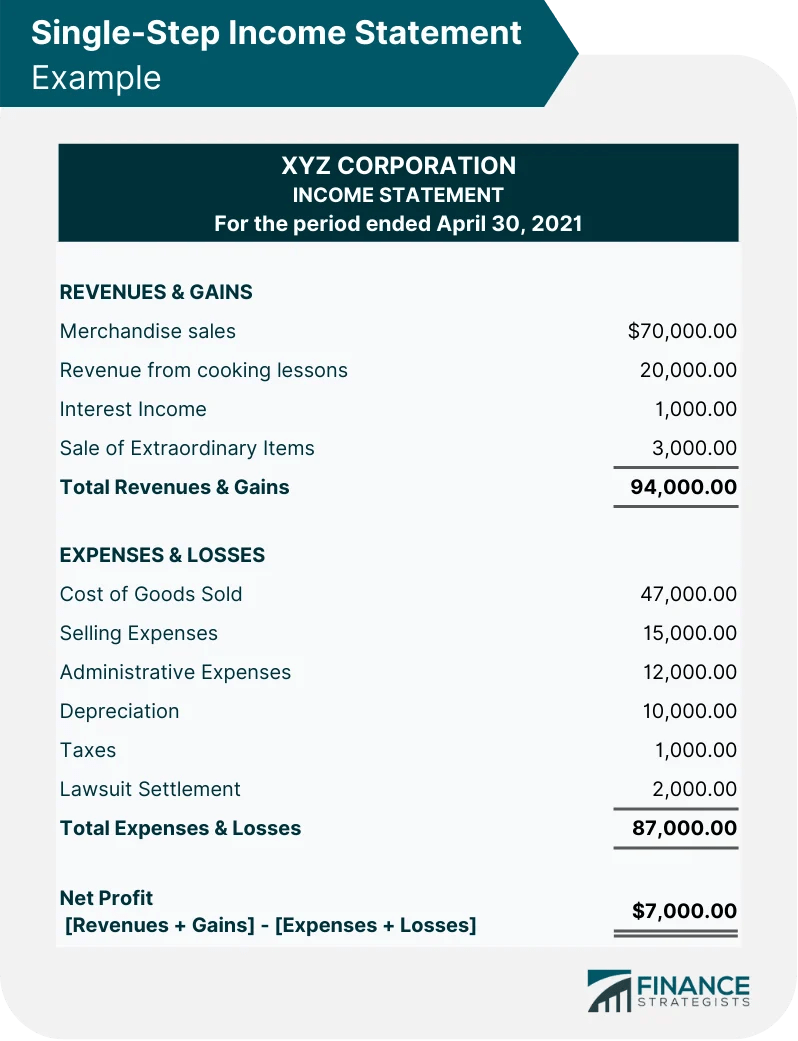
Example of a Single-Step Income Statement
The single-step income statement lumps together all of XYZ Corporation’s revenues and gains and these amounted to $94,000.
Its expenses and losses are also lumped together totaling $87,000.
Using the net profit formula we had above, we find that:
Net Profit = (Revenues + Gains) – (Expenses + Losses)
= 94,000 - 87,000
= $7,000.00
Importance of Income Statements
Income statements are generally used to serve as a reporting metric for various stakeholders.
It provides them with a summary of the performance of the company during a specific period.
The income statement benefits various stakeholders in several ways.
These include:
Management
With the income statement detailing the categories of revenues and expenses of a company, management is able to see how each department of a company is performing.
It helps managers and business owners point out which company expenses are growing at an unexpected rate and which of these expenses need to be cut down in the future.
Directors and executives are also provided a clear picture of the performance of the company as a whole during a specific accounting period.
Income statements serve as an indicator of how successful the implemented strategies are and whether there are areas that need improvement.
Investors
Income statements also provide a good source of analysis for investors that are willing to invest in the business.
Typically, investors prefer looking at a company’s operating profit figure rather than a company’s bottom line as it gives them a better idea of how much money the company is making from its core operations.
Lenders & Creditors
Financial institutions or lenders demand the income statement of a company before they release any loan or credit to the business.
This is because lenders want to know the ability of the company to generate revenue and profit, as well as its capacity to repay the loan.
Analysts
The income statement is also vital for ratio analysis, equity research, and valuation of the company.
It helps analysts and research houses analyze, forecast, and perform corporate valuation in order to create future economic decisions in the company.
Conclusion
An income statement is one of the most important financial statements for a company.
It provides insights into a company's overall profitability and helps investors evaluate a company's financial performance.
Income statements can be complex, but understanding the different components is crucial to interpretation.
Income statements provide a summary of the performance of a company during a specific accounting period and are useful for various stakeholders like management, investors, lenders, and creditors.
It can also be used to make decisions about inorganic or organic growth, company strategies, and analyst consensus.
Income statements are an essential part of a company's financial reporting.
While an Income statement is vital for the business, it should be noted that an Income statement is just one of the three financial statements.
The other two important financial statements are the balance sheet and cash flow statement.
All three documents must be reviewed together to get a clear picture of the financial health of the business.
An income statement should be used in conjunction with the other two financial statements.
Income Statement FAQs
An Income Statement is a financial statement that shows the revenues and expenses of a company over a specific accounting period. It tells whether a company has made a profit or loss during that period.
Income statement evaluates the profit or loss of a business over a period of time, whereas balance sheets show the financial position of a business at a specific point in time.
Income statements are important because they show the overall profitability of a company and help investors evaluate a company's financial performance. Income statements can also be used to make decisions about inorganic or organic growth, company strategies, and analyst consensus.
EBITDA is not normally included in the income statement of a company because it is not a metric accepted by Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) as a measure of financial performance. However, EBITDA can be calculated using the information from the income statement.
Revenue, cost of goods sold, gross profit, selling, general and administrative expenses, depreciation and amortization expense, operating profit, interest expense, other expenses, earnings before taxes, and income taxes are the common items included in an income statement.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.
