Financial statements are key tools businesses use to track and provide insights into a company's overall financial performance and health. These reports provide a snapshot of a business’s financial situation, results of operations, and cash flows. While financial statements are used internally to guide management decisions, they are also used by external stakeholders such as investors, creditors, analysts, and regulators. Financial statements aid in making decisions about investing in a company, lending money to a company, or providing other forms of financing. There are three main types of financial statements: balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow statements. These are compiled using Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP). GAAP is a set of guidelines and standards U.S.-based companies must follow when preparing their financial statements. The balance sheet is a financial statement that provides an overview of a company's assets, liabilities, and equity. It is used to assess a company's financial situation at a given point in time. There are two sections on the balance sheet ‒ the left side (assets) and the right side (liabilities and equity). The balance sheet adheres to the accounting equation: The assets of a company should always equal the combination of its liabilities and shareholders' equity. Hence, a balance sheet should always balance. For example, a company purchases equipment on credit for $2,000. This purchase will entail an increase in assets (equipment) and a liability (credit purchase) for the amount of $2,000. The company's assets would then equal its liabilities plus shareholders' equity. Assets, liabilities, and equity comprise the balance sheet. Assets are everything a company owns and can be used to generate revenue. They include cash, investments, inventory, and property, plant, & equipment (PP&E). Liabilities are everything a company owes to others. These include accounts payables, loans, and notes payables. Equity is the portion of the business that belongs to the owners (i.e., shareholders). Equity is also known as a company's book value or net worth. It represents the residual value of a company's assets after liabilities have been paid. It includes retained earnings, paid-in capital, outstanding shares, and treasury stock. The following is an example of a balance sheet from Apple, Inc.: Source: Apple’s Form 10-k from SEC (Page 34) From the balance sheet above, we can see that as of September 2021, Apple, Inc.’s total assets amount to $351,002,000. Its total liabilities are $287,912,000, and total shareholders’ equity is $63,090,000, which, when lumped together, will equal the total assets of $351,002,000.What Are Financial Statements?
Balance Sheet

Components of a Balance Sheet
Assets
Liabilities
Equity
Balance Sheet Example

Income Statement
The income statement is a financial statement that reports a company's revenue, expenses, and profit (or loss) over a period of time.
It is also known as the profit and loss (P&L) statement and is important in gauging the profitability of a business.
Components of an Income Statement
The components of an income statement vary depending on the company but below are some of the most common items:
Revenue
Revenue pertains to the money a company earns from selling its goods or services. Depending on the company, revenue can also be called “sales revenue” or “sales.”
Revenue is typically listed as net sales as it would exclude any applicable sales returns, allowances, and discounts before cost of goods sold is deducted to arrive at gross profit.
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
COGS refers to the direct costs associated with the production of a good. This is known as the cost of sales for businesses that provide services. This includes the cost of direct materials, direct labor, and direct factory overhead.
Gross Profit
Gross profit is the difference between a company's revenue (net sales) and the cost of goods sold. It reflects the efficiency of a company in its production and selling process.
Operating Expenses
Operating expenses are the costs associated with managing a business on a day-to-day basis. These are costs that consist of the direct costs involved in the production of a company’s products and services but are not included in COGS.
They include things like rent, utilities, and salaries/wages.
Selling, general, and administrative (SG&A) expenses, in other words, all non-production costs, are usually lumped together with operating expenses. Some companies also choose to put this as a separate line item from operating expenses.
Operating Profit
Operating profit is a company's income after deducting all operating expenses from the gross profit.
Non-Operating Items
Non-operating items are all the other revenues and expenses that are not part of the business's main operations. These include interest expenses, interest income, proceeds from sale of extraordinary items, lawsuit expenses, and taxes.
Net Profit or Loss
This is the amount of money a company has left over after taking into account all non-operating items from the operating profit. It is the income statement's bottom line and represents the company's total earnings or losses for a period of time.
Net profit occurs when a company’s revenues exceed its expenses. Net loss occurs when it is the other way around.
Income Statement Example
Shown below is the income statement from Apple, Inc.

Source: Apple’s Form 10-k from SEC (Page 32)
Per the income statement above, Apple, Inc.’s gross profit as of September 2021 was $152,836,000, the operating profit was $108,949,000, and the net profit was $94,680,000.
This means the company has a profit margin of 26% which is the percentage of its net profit from total sales.
Cash Flow Statement
A cash flow statement is another type of financial statement that provides a snapshot of a business's cash inflow and outflow during a specific period. This statement shows how much cash is being generated or used by a company, and can be used to assess its financial health.
Components of a Cash Flow Statement
A cash flow statement has these main components:
Cash Flow From Operating Activities (CFO)
This demonstrates the amount of cash generated by the business or used from its ongoing business operations. This can include salaries paid to employees, payments from customers, and cash paid to suppliers.
A company's operating cash flow is a key metric in assessing the financial viability of its core operations.
Cash Flow From Investing Activities (CFI)
This indicates how much cash the company has generated or used from investing activities. This can include things like buying property, plant, & equipment or investing in securities.
Companies use CFI to assess their ability to generate cash from their investments and to make decisions about future investment opportunities.
Cash Flow From Financing Activities (CFF)
This indicates the amount of money the company has generated or used from its financing activities. This can include issuing new equity, taking out loans, or repaying debt.
Companies use CFF to assess their operations' ability to finance and make decisions about issuing new equity and debt financing.
Cash Flow Statement Example
The following is an example of a cash flow statement of Apple, Inc.
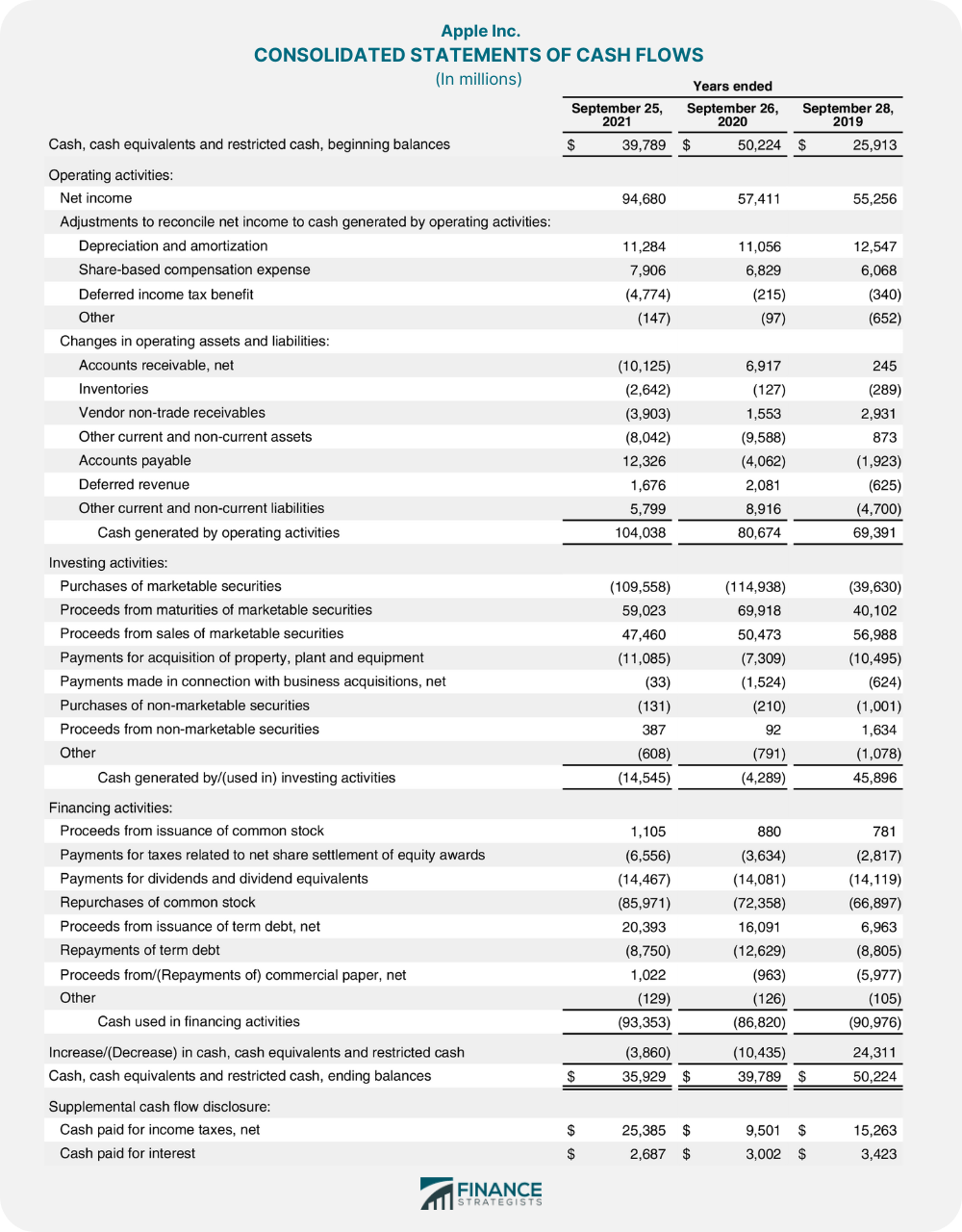
Source: Apple’s Form 10-k from SEC (Page 36)
Based on the cash flow statement above, Apple, Inc.’s total CFO for September 2021 was $104,038,000. They used $14,545,000 for their investing activities and $93,353,000 in financing activities.
The total decrease in cash, cash equivalents, and restricted cash was $3,860,000. The total ending balance was $35,929,000 after deducting the said decrease from its beginning balance.
Limitations of Financial Statements
Financial statements are useful tools for analyzing a company's financial position, performance, and cash flow. However, several limitations should be considered when interpreting the data.
First, financial statements only provide a snapshot of a company's financial position at a specific point in time. They do not reveal how the company got to that point or what might happen in the future.
Second, financial statements only include information that can be quantified in monetary terms. This means the numbers do not reflect vital information like customer satisfaction or employee morale.
Third, management can manipulate financial statements to give a false impression of the company's financial health. For example, a company might recognize revenue early or delay expenses to make the financials look better than they actually are.
Fourth, financial statements only provide limited information about a company's competitive position. They do not reveal things like market share or brand awareness.
Finally, financial statements can be difficult to interpret without a basic understanding of accounting principles. This makes them inaccessible to many people who could benefit from using them.
Despite their limitations, financial statements are still valuable tools for analyzing a company's financial situation. When interpreting the data, it is important to consider the limitations of the information and use other resources to supplement the analysis.
Conclusion
Financial statements are records of a company’s financial activities and are used to reflect its performance.
The three main financial statements are the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement. These statements are vital for understanding a company's financial situation, performance, and cash flow.
It is essential to keep in mind that financial statements have limitations. They should be used in conjunction with other financial information to get a complete picture of a company's financial situation.
Financial Statements FAQs
Financial statements are important because they provide a snapshot of a company's financial position at a specific point in time. They can be used to assess a company's financial health, performance, and cash flow.
Most companies prepare financial statements on a quarterly or annual basis. However, some companies may prepare them more frequently if they are required to do so.
The accuracy of financial statements is only as good as the information utilized to prepare them. The financial statements will also be inaccurate if a company's accounting records are inaccurate.
Financial statements can be used to assess a company's financial health, performance, and cash flow. This information can be used to make informed business decisions about things like investment opportunities, pricing strategies, and expense management.
Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) are guidelines that companies must follow when preparing financial statements. GAAP includes standards for things like recognition, measurement, and disclosure. GAAP can impact financial statements on how revenue is recognized and expenses are reported. Following GAAP ensures that financial statements are consistent and comparable.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.
