Mark Henricks
·5 min read
When C corporations pay dividends to shareholders, the transactions get reported to both the shareholder and the Internal Revenue Service using Form 1099-DIV. This form gives the amount of the dividend as well as the classification of the dividend, which is important for determining how it will be taxed. Here’s what you need to know about reporting C corporation dividends to shareholders.
A financial advisor could help you optimize an investment strategy to minimize your tax liability.
Dividend Reporting Basics
Dividends paid by C corporations can represent an important source of income for individual investors. C corporations have to pay income taxes on their earnings and profits before paying dividends and the dividends paid to shareholders are not deductible as expenses on C corporation tax returns. That means dividends are subject to double taxation, as the shareholders also report and pay taxes on the dividends they receive.
ADVERTIsem*nT
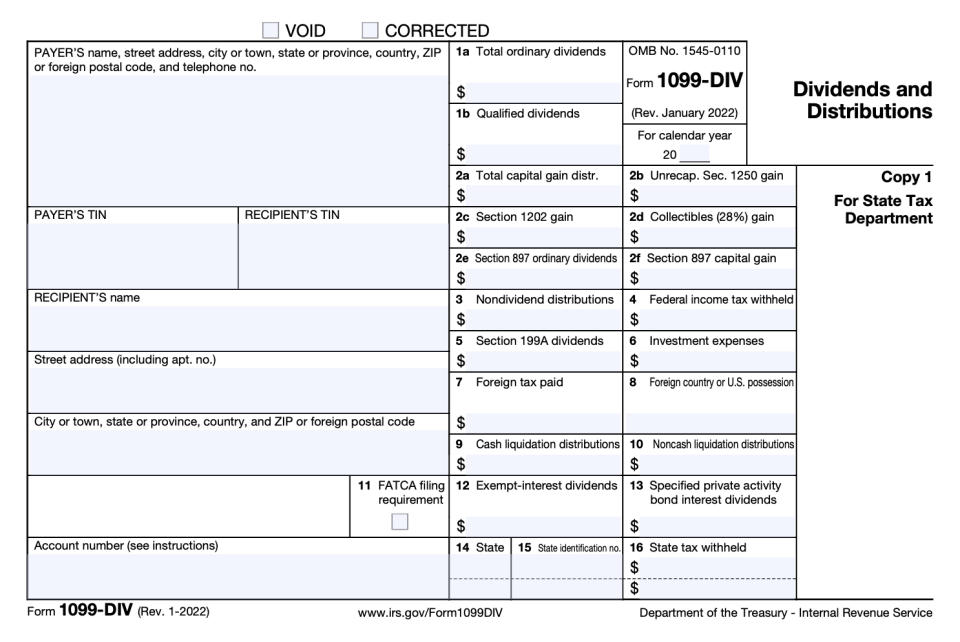
A shareholder who gets at least $10 in dividends will receive a copy of Form 1099-DIV from the C corporation that pays the dividend. In addition to C corporate dividends, the same form is used to report other types of income, including distributions from retirement accounts and lawsuit settlements. If you have shares in more than one C corporation that pays dividends, you will get a different 1099-DIV from each one that paid you more than $10 in dividends from that corporation.
Copies of this form, which reports the dividends paid during the previous calendar year as well as their classification for tax purposes, will also go to the IRS as well as state and local income tax authorities. The taxpayer who receives the 1099-DIV doesn’t need to send the form in with their tax return. Instead, the taxpayer uses the information on the form to fill out the tax return.
If the corporation that pays the dividend doesn’t send a 1099-DIV, the taxpayer is still required to report the dividend income for tax purposes. This includes dividends that do not meet the $10 threshold for sending 1099-DIV. If a taxpayer is expecting a 1099-DIV from a corporation and doesn’t receive it soon after the January 31 deadline for sending it, it is appropriate to contact the corporation and request a copy.
Dividend Reporting Details
The Form 1099-DIV will report dividends as being one of several different types. The most common type is ordinary dividends. These are shown in Box 1a on the form. Ordinary dividends are usually taxed as ordinary income at the taxpayer’s usual rate.
Don't miss out on news that could impact your finances. Get news and tips to make smarter financial decisions with SmartAsset's semi-weekly email. It's 100% free and you can unsubscribe at any time. Sign up today.
Other types of dividends reported on 1099-DIV include qualified dividends, which are in Box 1b. Qualified dividends generally get taxed at the capital gains rate of 0% to 20%, which is typically lower than the rate the taxpayer pays on ordinary income.
Some additional types of income beyond C corporation dividends are also reported on the 1099-DIV. These include capital gains distributions from mutual funds and exchange-traded funds, dividends paid by Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) and tax-exempt dividends.
Taxpayers report dividend income on Form 1040 of their tax return. Ordinary dividend income goes on Line 3b of the Form 1040. Qualified dividends get entered on Line 3a of the same form.
If a taxpayer receives more than $1,500 of ordinary dividends, the taxpayer also is required to complete Schedule B of the Form 1040 and attach it to their return. On the Schedule B, the taxpayer lists the name of the corporation that paid the dividend as well as the amount of ordinary dividends.
Taxpayers report any qualified dividends from Box 1b of the Form 1099-DIV on line 3a of their Form 1040. To figure the tax on this income, taxpayers usually use the Qualified Dividends and Capital Gain Tax Worksheet that is part of the Form 1040.
Sometimes owners of closely held C corporations may elect to receive larger salaries because salaries are deductible expenses on the C corporation’s return. This helps to reduce the double taxation effect. However, the salaries paid have to be reasonable, according to the IRS definition, or the taxing authority may reclassify some of the salary as a dividend, increasing the corporation’s taxable income.
Bottom Line
Dividends paid by C corporations will be reported to shareholders using Form 1099-DIV. The C corporation will also send a copy of the form listing dividends to the IRS and other income tax agencies The recipient of the dividends is required to report these dividends using the information on the 1099-DIV. Dividends will be classified as ordinary or qualified, which may affect how they are reported on the taxpayers return and the amount of tax that will be due.
Tax Planning Tips for Investors
A financial advisor can help you optimize your investment plan to lower taxes. SmartAsset’s free tool matches you with up to three financial advisorswho serve your area, and you can interview your advisor matches at no cost to decide which one is right for you. If you’re ready to find an advisor who can help you achieve your financial goals, get started now.
SmartAsset’s income tax calculator helps you figure out how much tax you are likely to owe based on your specific situation.
Photo credit: ©iStock.com/damircudic, ©iStock.com/IRS.gov, ©iStock.com/designer491
The post Reporting C Corporation Dividends to Shareholders appeared first on SmartAsset Blog.